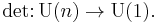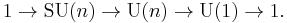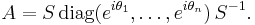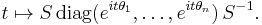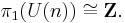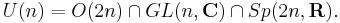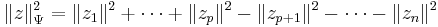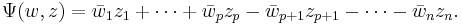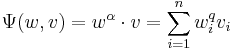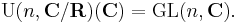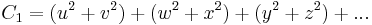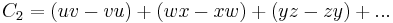Unitary group
| Group theory |
|---|
| Group theory |
|
Cyclic group Zn
Symmetric group, Sn Dihedral group, Dn Alternating group An Mathieu groups M11, M12, M22, M23, M24 Conway groups Co1, Co2, Co3 Janko groups J1, J2, J3, J4 Fischer groups F22, F23, F24 Baby Monster group B Monster group M |
|
|
|
Solenoid (mathematics)
Circle group General linear group GL(n) Special linear group SL(n) Orthogonal group O(n) Special orthogonal group SO(n) Unitary group U(n) Special unitary group SU(n) Symplectic group Sp(n) Lorentz group Poincaré group Conformal group Diffeomorphism group Loop group Infinite-dimensional Lie groups O(∞) SU(∞) Sp(∞) |
| Lie groups |
|---|
|
General linear group GL(n)
Special linear group SL(n) Orthogonal group O(n) Special orthogonal group SO(n) Unitary group U(n) Special unitary group SU(n) Symplectic group Sp(n) |
In mathematics, the unitary group of degree n, denoted U(n), is the group of n×n unitary matrices, with the group operation that of matrix multiplication. The unitary group is a subgroup of the general linear group GL(n, C). Hyperorthogonal group is an archaic name for the unitary group, especially over finite fields.
In the simple case n = 1, the group U(1) corresponds to the circle group, consisting of all complex numbers with absolute value 1 under multiplication. All the unitary groups contain copies of this group.
The unitary group U(n) is a real Lie group of dimension n2. The Lie algebra of U(n) consists of complex n×n skew-Hermitian matrices, with the Lie bracket given by the commutator.
The general unitary group (also called the group of unitary similitudes) consists of all matrices  such that
such that 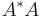 is a nonzero multiple of the identity matrix, and is just the product of the unitary group with the group of all positive multiples of the identity matrix.
is a nonzero multiple of the identity matrix, and is just the product of the unitary group with the group of all positive multiples of the identity matrix.
Contents |
Properties
Since the determinant of a unitary matrix is a complex number with norm 1, the determinant gives a group homomorphism
The kernel of this homomorphism is the set of unitary matrices with determinant 1. This subgroup is called the special unitary group, denoted SU(n). We then have a short exact sequence of Lie groups:
This short exact sequence splits so that U(n) may be written as a semidirect product of SU(n) by U(1). Here the U(1) subgroup of U(n) consists of matrices of the form diag(eiθ, 1, 1, ..., 1).
The unitary group U(n) is nonabelian for n > 1. The center of U(n) is the set of scalar matrices λI with λ ∈ U(1). This follows from Schur's lemma. The center is then isomorphic to U(1). Since the center of U(n) is a 1-dimensional abelian normal subgroup of U(n), the unitary group is not ‹The template Dab button is being considered for deletion.› [//toolserver.org/~dispenser/cgi-bin/dab_solver.py?page=Unitary_group&editintro=Template:Disambiguation_needed/editintro&client=Dab_button&fixlinks=semisimple ].
Topology
The unitary group U(n) is endowed with the relative topology as a subset of Mn(C), the set of all n×n complex matrices, which is itself homeomorphic to a 2n2-dimensional Euclidean space.
As a topological space, U(n) is both compact and connected. The compactness of U(n) follows from the Heine-Borel theorem and the fact that it is a closed and bounded subset of Mn(C). To show that U(n) is connected, recall that any unitary matrix A can be diagonalized by another unitary matrix S. Any diagonal unitary matrix must have complex numbers of absolute value 1 on the main diagonal. We can therefore write
A path in U(n) from the identity to A is then given by
The unitary group is not simply connected; the fundamental group of U(n) is infinite cyclic for all n:
The first unitary group U(1) is topologically a circle, which is well known to have a fundamental group isomorphic to Z, and the inclusion map 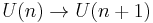 is an isomorphism on
is an isomorphism on 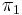 . (It has quotient the Stiefel manifold.)
. (It has quotient the Stiefel manifold.)
The determinant map 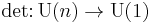 induces an isomorphism of fundamental groups, with the splitting
induces an isomorphism of fundamental groups, with the splitting 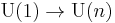 inducing the inverse.
inducing the inverse.
Related groups
2-out-of-3 property
The unitary group is the 3-fold intersection of the orthogonal, symplectic, and complex groups:
Thus a unitary structure can be seen as an orthogonal structure, a complex structure, and a symplectic structure, which are required to be compatible (meaning that one uses the same J in the complex structure and the symplectic form, and that this J is orthogonal; writing all the groups as matrix groups fixes a J (which is orthogonal) and ensures compatibility).
In fact, it is the intersection of any two of these three; thus a compatible orthogonal and complex structure induce a symplectic structure, and so forth. [1] [2]
At the level of equations, this can be seen as follows:
- Symplectic:
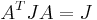
- Complex:
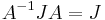
- Orthogonal:
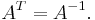
Any two of these equations implies the third.
At the level of forms, this can be seen by decomposing a Hermitian form into its real and imaginary parts: the real part is symmetric (orthogonal), and the imaginary part is skew-symmetric (symplectic)—and these are related by the complex structure (which is the compatibility). On an almost Kähler manifold, one can write this decomposition as 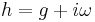 , where h is the Hermitian form, g is the Riemannian metric, i is the almost complex structure, and
, where h is the Hermitian form, g is the Riemannian metric, i is the almost complex structure, and 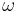 is the almost symplectic structure.
is the almost symplectic structure.
From the point of view of Lie groups, this can partly be explained as follows: 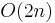 is the maximal compact subgroup of
is the maximal compact subgroup of 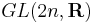 , and
, and 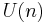 is the maximal compact subgroup of both
is the maximal compact subgroup of both 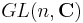 and
and 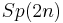 . Thus the intersection of
. Thus the intersection of 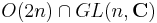 or
or 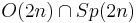 is the maximal compact subgroup of both of these, so
is the maximal compact subgroup of both of these, so 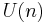 . From this perspective, what is unexpected is the intersection
. From this perspective, what is unexpected is the intersection 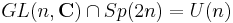 .
.
Special unitary and projective unitary groups
Just as the orthogonal group has the special orthogonal group SO(n) as subgroup and the projective orthogonal group PO(n) as quotient, and the projective special orthogonal group PSO(n) as subquotient, the unitary group has associated to it the special unitary group SU(n), the projective unitary group PU(n), and the projective special unitary group PSU(n). These are related as by the commutative diagram at right; notably, both projective groups are equal: 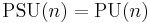 .
.
The above is for the classical unitary group (over the complex numbers) – for unitary groups over finite fields, one similarly obtains special unitary and projective unitary groups, but in general 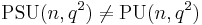 .
.
G-structure: almost Hermitian
In the language of G-structures, a manifold with a 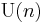 -structure is an almost Hermitian manifold.
-structure is an almost Hermitian manifold.
Generalizations
From the point of view of Lie theory, the classical unitary group is a real form of the Steinberg group 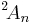 , which is an algebraic group that arises from the combination of the diagram automorphism of the general linear group (reversing the Dynkin diagram
, which is an algebraic group that arises from the combination of the diagram automorphism of the general linear group (reversing the Dynkin diagram 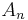 , which corresponds to transpose inverse) and the field automorphism of the extension
, which corresponds to transpose inverse) and the field automorphism of the extension 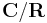 (namely complex conjugation). Both these automorphisms are automorphisms of the algebraic group, have order 2, and commute, and the unitary group is the fixed points of the product automorphism, as an algebraic group. The classical unitary group is a real form of this group, corresponding to the standard Hermitian form
(namely complex conjugation). Both these automorphisms are automorphisms of the algebraic group, have order 2, and commute, and the unitary group is the fixed points of the product automorphism, as an algebraic group. The classical unitary group is a real form of this group, corresponding to the standard Hermitian form 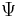 , which is positive definite.
, which is positive definite.
This can be generalized in a number of ways:
- generalizing to other Hermitian forms yields indefinite unitary groups
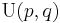 ;
; - the field extension can be replaced by any degree 2 separable algebra, most notably a degree 2 extension of a finite field;
- generalizing to other diagrams yields other groups of Lie type, namely the other Steinberg groups
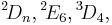 (in addition to
(in addition to 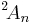 ) and Suzuki-Ree groups
) and Suzuki-Ree groups
- considering a generalized unitary group as an algebraic group, one can take its points over various algebras.
Indefinite forms
Analogous to the indefinite orthogonal groups, one can define an indefinite unitary group, by considering the transforms that preserve a given Hermitian form, not necessarily positive definite (but generally taken to be non-degenerate). Here one is working with a vector space over the complex numbers.
Given a Hermitian form 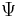 on a complex vector space
on a complex vector space 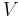 , the unitary group
, the unitary group 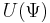 is the group of transforms that preserve the form: the transform
is the group of transforms that preserve the form: the transform  such that
such that 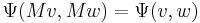 for all
for all 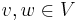 . In terms of matrices, representing the form by a matrix denoted
. In terms of matrices, representing the form by a matrix denoted 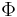 , this says that
, this says that 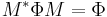 .
.
Just as for symmetric forms over the reals, Hermitian forms are determined by signature, and are all unitarily congruent to a diagonal form with 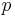 entries of 1 on the diagonal and
entries of 1 on the diagonal and 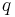 entries of
entries of 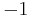 . The non-degenerate assumption is equivalent to
. The non-degenerate assumption is equivalent to 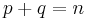 . In a standard basis, this is represented as a quadratic form as:
. In a standard basis, this is represented as a quadratic form as:
and as a symmetric form as:
The resulting group is denoted 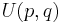 .
.
Finite fields
Over the finite field with 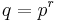 elements,
elements, 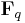 , there is a unique degree 2 extension field,
, there is a unique degree 2 extension field, 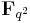 , with order 2 automorphism
, with order 2 automorphism 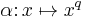 (the
(the 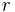 th power of the Frobenius automorphism). This allows one to define a Hermitian form on an
th power of the Frobenius automorphism). This allows one to define a Hermitian form on an 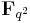 vector space
vector space 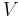 , as an
, as an 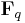 -bilinear map
-bilinear map 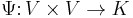 such that
such that 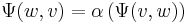 and
and  for
for 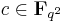 . Further, all non-degenerate Hermitian forms on a vector space over a finite field are unitarily congruent to the standard one, represented by the identity matrix, that is, any Hermitian form is unitarily equivalent to
. Further, all non-degenerate Hermitian forms on a vector space over a finite field are unitarily congruent to the standard one, represented by the identity matrix, that is, any Hermitian form is unitarily equivalent to
where 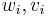 represent the coordinates of
represent the coordinates of 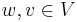 in some particular
in some particular 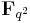 -basis of the
-basis of the  -dimensional space
-dimensional space 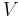 (Grove 2002, Thm. 10.3).
(Grove 2002, Thm. 10.3).
Thus one can define a (unique) unitary group of dimension  for the extension
for the extension 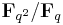 , denoted either as
, denoted either as 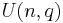 or
or 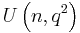 depending on the author. The subgroup of the unitary group consisting of matrices of determinant 1 is called the special unitary group and denoted
depending on the author. The subgroup of the unitary group consisting of matrices of determinant 1 is called the special unitary group and denoted 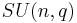 or
or 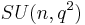 . For convenience, this article will use the
. For convenience, this article will use the 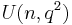 convention. The center of
convention. The center of 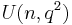 has order
has order 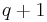 and consists of the scalar matrices which are unitary, that is those matrices
and consists of the scalar matrices which are unitary, that is those matrices 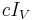 with
with 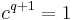 . The center of the special unitary group has order
. The center of the special unitary group has order 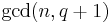 and consists of those unitary scalars which also have order dividing
and consists of those unitary scalars which also have order dividing  . The quotient of the unitary group by its center is called the projective unitary group,
. The quotient of the unitary group by its center is called the projective unitary group, 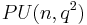 , and the quotient of the special unitary group by its center is the projective special unitary group
, and the quotient of the special unitary group by its center is the projective special unitary group 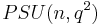 . In most cases (
. In most cases (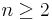 and
and 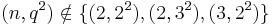 ),
), 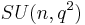 is a perfect group and
is a perfect group and 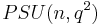 is a finite simple group, (Grove 2002, Thm. 11.22 and 11.26).
is a finite simple group, (Grove 2002, Thm. 11.22 and 11.26).
Degree-2 separable algebras
More generally, given a field k and a degree-2 separable k-algebra K (which may be a field extension but need not be), one can define unitary groups with respect to this extension.
First, there is a unique k-automorphism of K 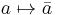 which is an involution and fixes exactly
which is an involution and fixes exactly 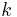 (
(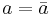 if and only if
if and only if 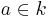 ).[3] This generalizes complex conjugation and the conjugation of degree 2 finite field extensions, and allows one to define Hermitian forms and unitary groups as above.
).[3] This generalizes complex conjugation and the conjugation of degree 2 finite field extensions, and allows one to define Hermitian forms and unitary groups as above.
Algebraic groups
The equations defining a unitary group are polynomial equations over 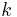 (but not over
(but not over 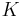 ): for the standard form
): for the standard form 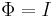 the equations are given in matrices as
the equations are given in matrices as 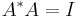 , where
, where 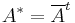 is the conjugate transpose. Given a different form, they are
is the conjugate transpose. Given a different form, they are 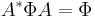 . The unitary group is thus an algebraic group, whose points over a
. The unitary group is thus an algebraic group, whose points over a 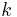 -algebra
-algebra 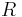 are given by:
are given by:
For the field extension 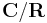 and the standard (positive definite) Hermitian form, these yield an algebraic group with real and complex points given by:
and the standard (positive definite) Hermitian form, these yield an algebraic group with real and complex points given by:
Polynomial invariants
The unitary groups are the automorphisms of two polynomials in real non-commutative variables:
These are easily seen to be the real and imginary parts of the complex form 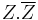 . The two invariants separately are invariants of O(2n) and Sp(2n,R). Combined they make the invariants of U(n) which is a subgroup of both these groups. The variables must be non-commutative in these invariants otherwise the second polynomial is identically zero.
. The two invariants separately are invariants of O(2n) and Sp(2n,R). Combined they make the invariants of U(n) which is a subgroup of both these groups. The variables must be non-commutative in these invariants otherwise the second polynomial is identically zero.
Classifying space
The classifying space for U(n) is described in the article classifying space for U(n).
See also
Notes
- ^ This is discussed in Arnold, "Mathematical Methods of Classical Mechanics".
- ^ symplectic
- ^ Milne, Algebraic Groups and Arithmetic Groups, p. 103
References
- Grove, Larry C. (2002), Classical groups and geometric algebra, Graduate Studies in Mathematics, 39, Providence, R.I.: American Mathematical Society, ISBN 978-0-8218-2019-3, MR1859189